Welcome to the website of Artbri Technology Limited !

Artbri Technology Limited
Focus on the development of sophisticated, digital and intelligent battery test equipment

Consulting Hotline (Mr. Liu):
+86 173-2848-0575
- home
-
Resistance test equipments
- Four probe resistance tester
- Four probe high resistance tester FTZ-45
- Four probe double electric resistance tester FTZ-42S
- Four-probe double electric resistance tester FTZ-45S
- Four probe double electric thickness resistance tester FTZ-42ST
- Four-probe double electric thickness and high resistance tester FTZ-45ST
- Soft pack battery voltage internal resistance tester SB-15
- Cylindrical battery voltage internal resistance testing machine YZ-20
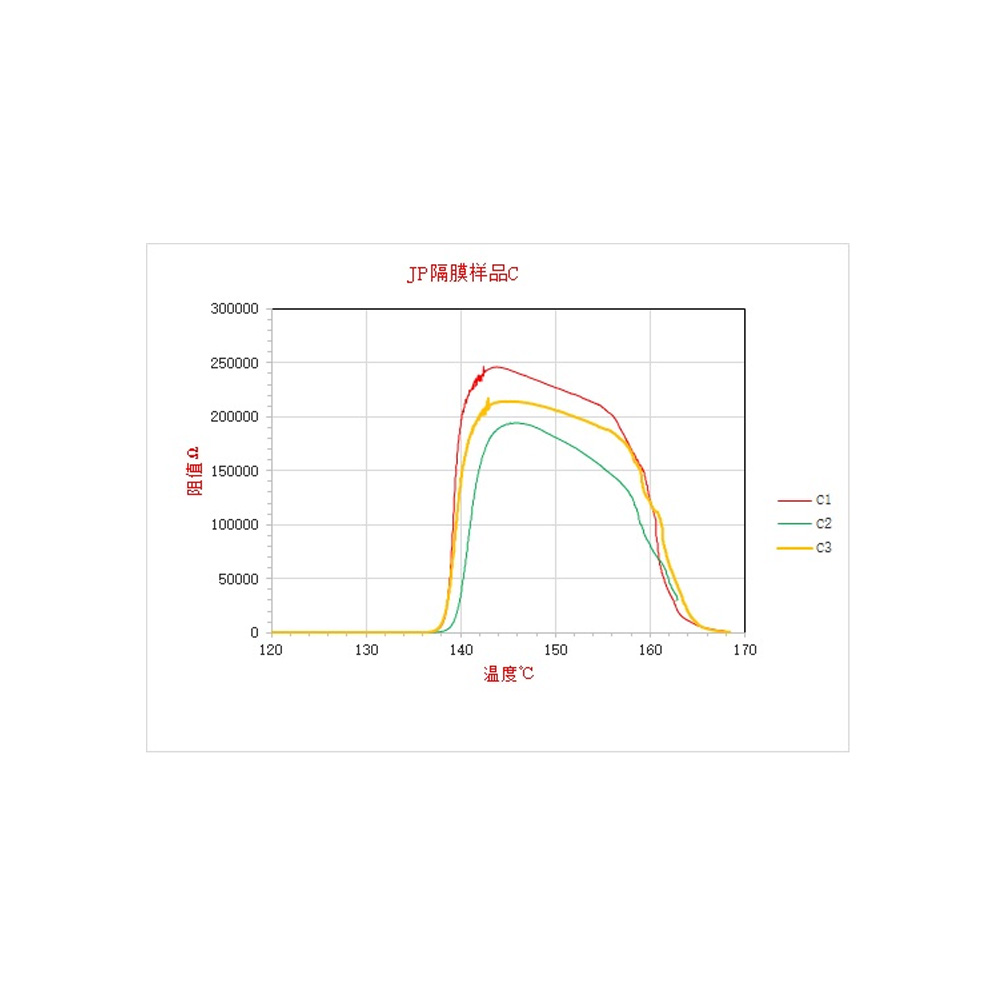
- Separator ion conductivity Tester
- Electrolyte high and low temperature saturated steamPressure & Conductivity conductivity tester
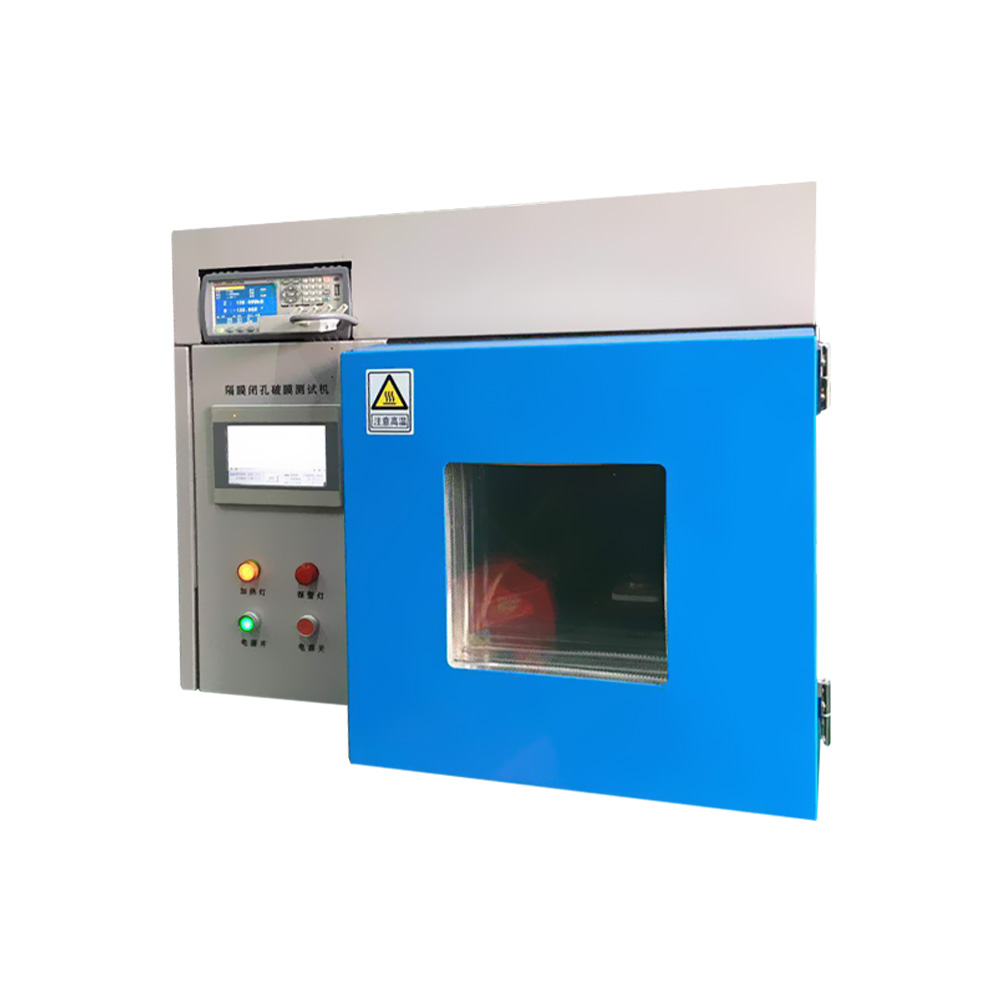
- Separator Shutdown & Break Tester closed cell rupture test machine ART-GMT-35L
- 5 ton Sheet & Powder resistance compaction density tester
- 1 tonSheet & Powder resistance compaction density tester
- Automatic Sheet resistance tester FTZ-45A
- Sheet Resistance Tester
-
Products
-
Temperature-controlled Altitude Simulation TesterTemperature-controlled low-pressure high-altitude testing machineBattery pack short circuit testing machinePurification fume hoodTemperature-controlled power battery short-circuit testing machineBattery explosion-proof boxPower battery automatic fire extinguishing and explosion-proof boxBattery thermal runaway gas production testerAutomatic fire extinguishing fume hoodCylindrical battery leakage and burst testing machineimpact testing machineBattery pack Seawater immersion test machineBattery pack fire test machineThree-box thermal shock testing machineThree-box temperature-controlled short-circuit testing machine100 ton temperature control servoCrush & Penetration punch testing machine
- Battery performance test equipments
- Lithium battery production equipments
- Custmized Automation equipments
- Tooling & Spare Parts for Battery Equipments
-
Temperature-controlled Altitude Simulation Tester
- Video Center
- News
- about us
- contact us